What Causes Artery Blockage?

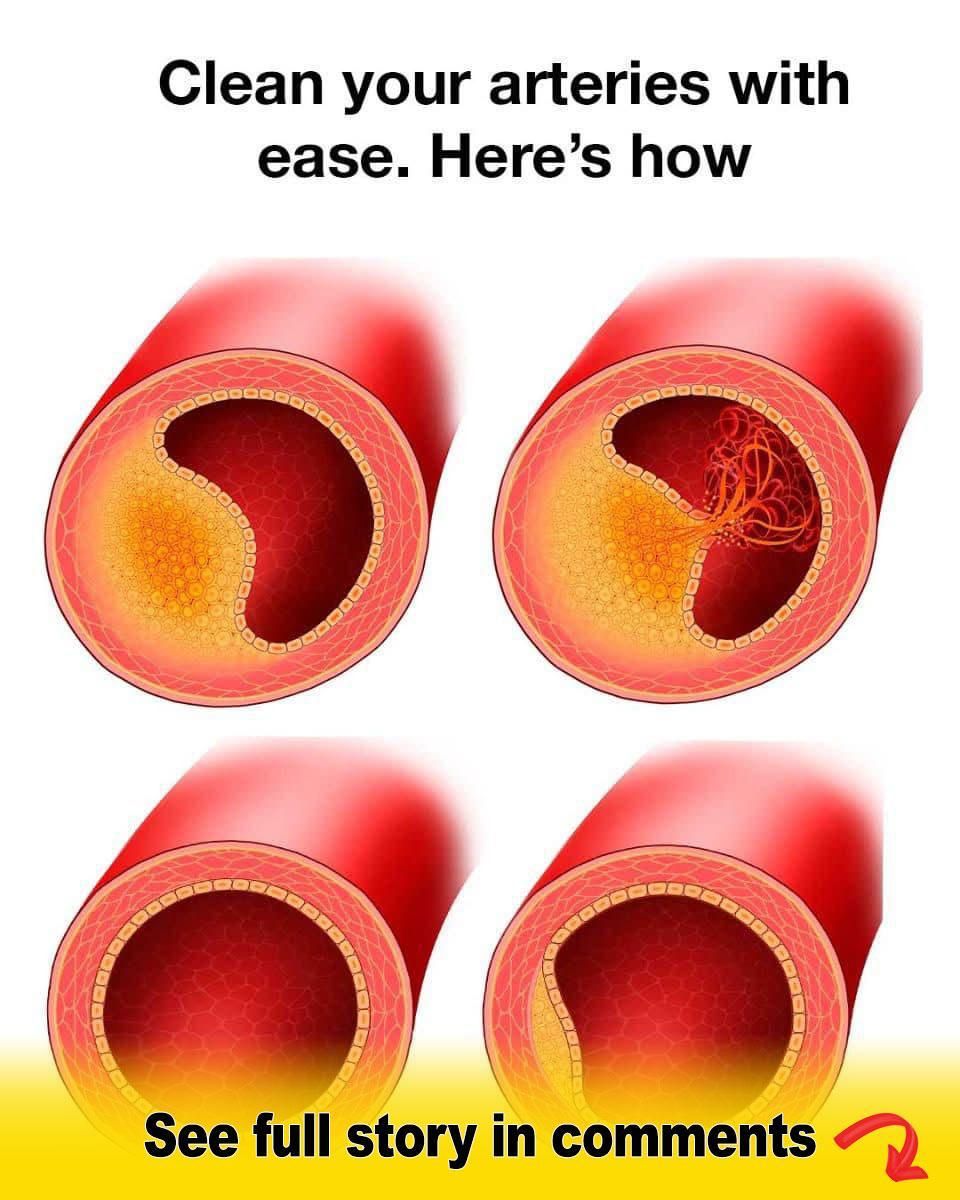
Atherosclerosis is often referred to as the hardening, thickening, and narrowing of the arteries. A thin layer of endothelial cells that help keep the inside of your arteries smooth and toned lines your arteries. This process allows your blood to keep flowing. However, several factors will damage the endothelial cells, including platelet cells, increased homocysteine levels, and free radicals from toxins and antioxidant deficiency. Also, vitamin C deficiency and homocysteine will damage the arteries from the degradation of a gel-like substance called the ground substance. It is found between the cells and helps maintain the integrity of the epithelial cell barrier.
The plaque will accumulate when various substances are unable to migrate out of the atherosclerotic lesion. These substances include fat, calcium, toxic metals, cellular waste, and cholesterol such as LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol. A material involved in blood clotting called fibrin is also accumulated when arteries are clogged. While the exact cause of clogged arteries is a mystery, evidence shows that atherosclerosis is a complex and slow condition that may begin in childhood and develop as you get older. Certain factors may damage your arteries’ inner layers, including smoking, high blood pressure, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and insulin resistance.
Other contributing factors of atherosclerosis include lack of exercise, being overweight, a type-A personality, heavy metal exposure, elevated triglycerides, and chronic inflammation from diseases, infections, lupus, or arthritis. High cholesterol and fats in the blood are also possible causes of atherosclerosis. On rare occasions, genetics may also play a factor with elevated production of cholesterol associated with atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis can also be caused by oxidative stress through the depletion of vitamin C or other antioxidants. Nutrient deficiencies or imbalances may also lead to atherosclerosis. They may include magnesium, potassium, fiber, antioxidants, and methyl donors. Dietary factors also include a diet high in sugar, processed starches, and damaged fats from overheating oils.[1,5,6]